Design and development of a new prototype of an intravascular device (stent) with variable radial force for stenotic lesions of carotid arteries
FUND AGENCY
| Spanish Ministry of Research and Innovation through the research project DPI2010-20746-C03-01 |   |
SUMMARY
This project will study, design, fabricate and experimentally test a new prototype of self-expanding stent with variable radial force throughout its length (larger in the medial zone), and therefore adapting this force to the type of stenotic injury. The stent will be made of Nitinol (a shape memory alloy) in such a way that it keeps constant force at the ends, allowing for a gradual remodelling of the vessel wall with a progressive opening of the zone of maximum stenosis (generally a hard calcic plaque) avoiding the need of balloon angioplasty.
This type of stenosis opening, would reduce endothelial damage and therefore re-stenosis by fibrosis. This stent design will be applied to carotid stenosis, a diseases responsible for 20-30% of cerebrovascular accidents (CVA), and the second cause of death and first cause of disability in adults in developed countries. Recent studies have put in evidence that the stenting technique with balloon, widely used in carotid artery, represents a considerable risk for patients. In order to attain this ambitious objective the project counts with a multidisciplinary team of engineers, medical doctors and veterinarians in such a way that all phases in the design of the new prototype can be completed, i.e., i) understanding of the problem and learning about actual medical devices, ii) familiarization and development of advance design tools (computational modelling, experimental tests, etc), iii) fabrication of the prototype, and iv) experimental validation in animal models, with further data analysis and stent designs.
 Carotid Stent Angioplasty |
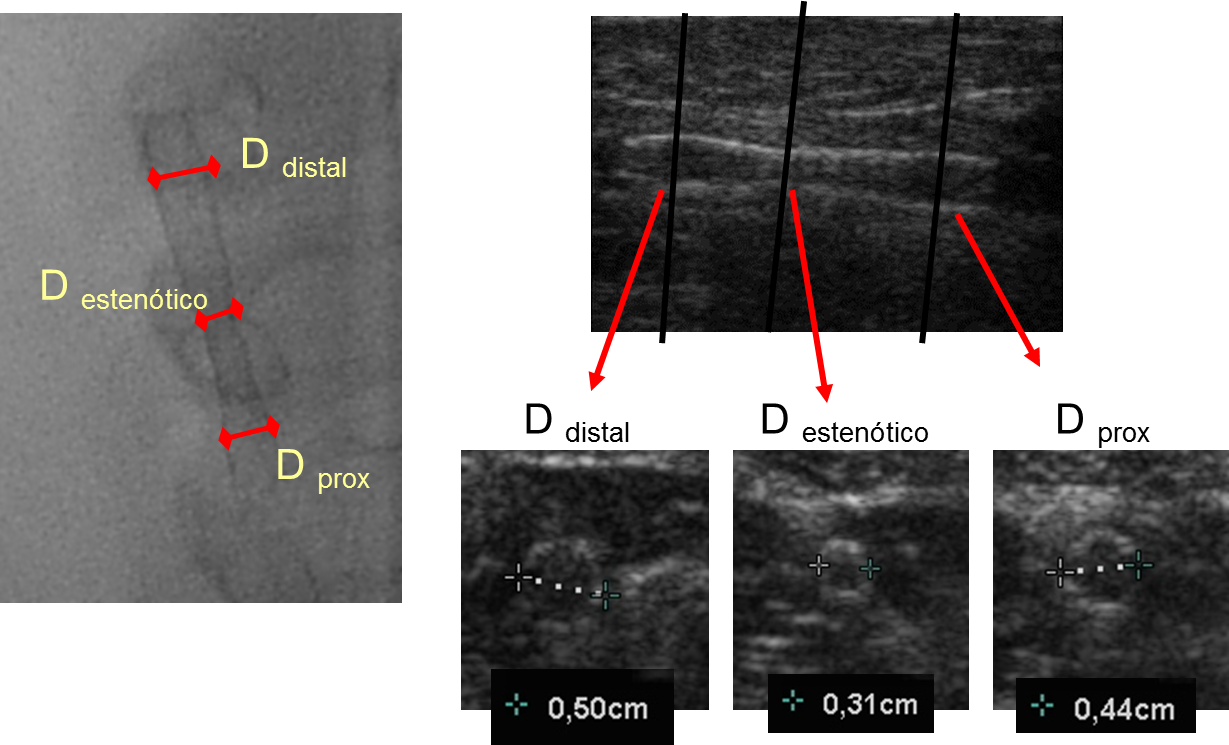
 CT Images of a Carotid Stenosis |
Different techniques are, therefore, combined at different phases of the project. First of all, the group of medical doctors, (interventionist radiologists, cardiologists and neurologists) will share with other team members their understanding of the stenosis problem, their experience with actual models of stent, clinical problems associated with their use, and other mechanical factors which significantly influence the success of angioplasty. The stent design will be performed with the aid of advanced finite element modelling of: the arterial wall, the atheromatous plaque and the mechanical behaviour of Nitinol. Experimental data for characterizing the mechanical behaviour of the vessels will be provided by veterinarians of the team. The developed models will be used to simulate stent deployment inside the stenosed artery and to find the optimum design capable of reducing the stenosis with minimum risk for the patient.
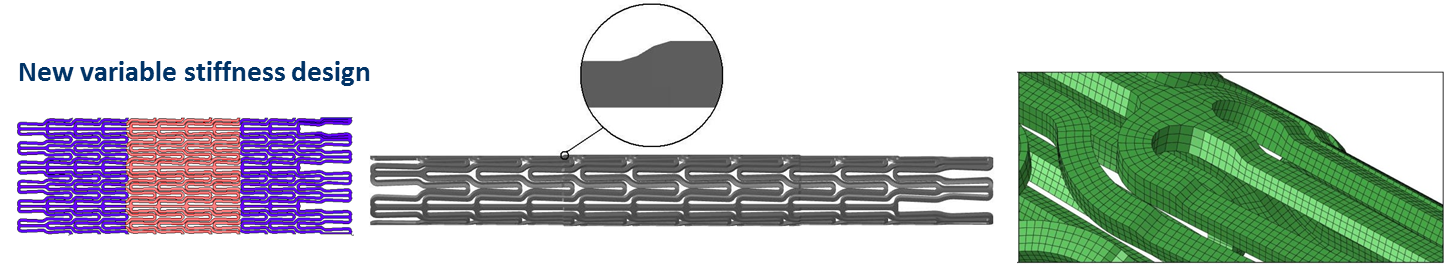
Sketch of the new Stent Design with VariableStiffness
|
|
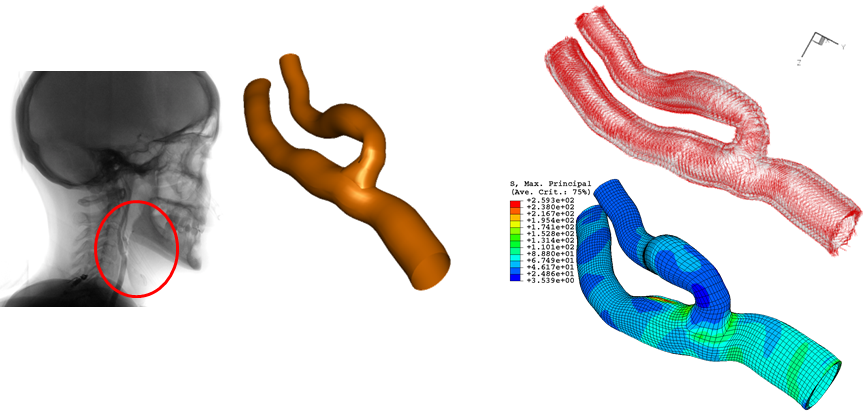
Geometric and FEM model of the Carotid Bifurcation. Fiber Orientation
|
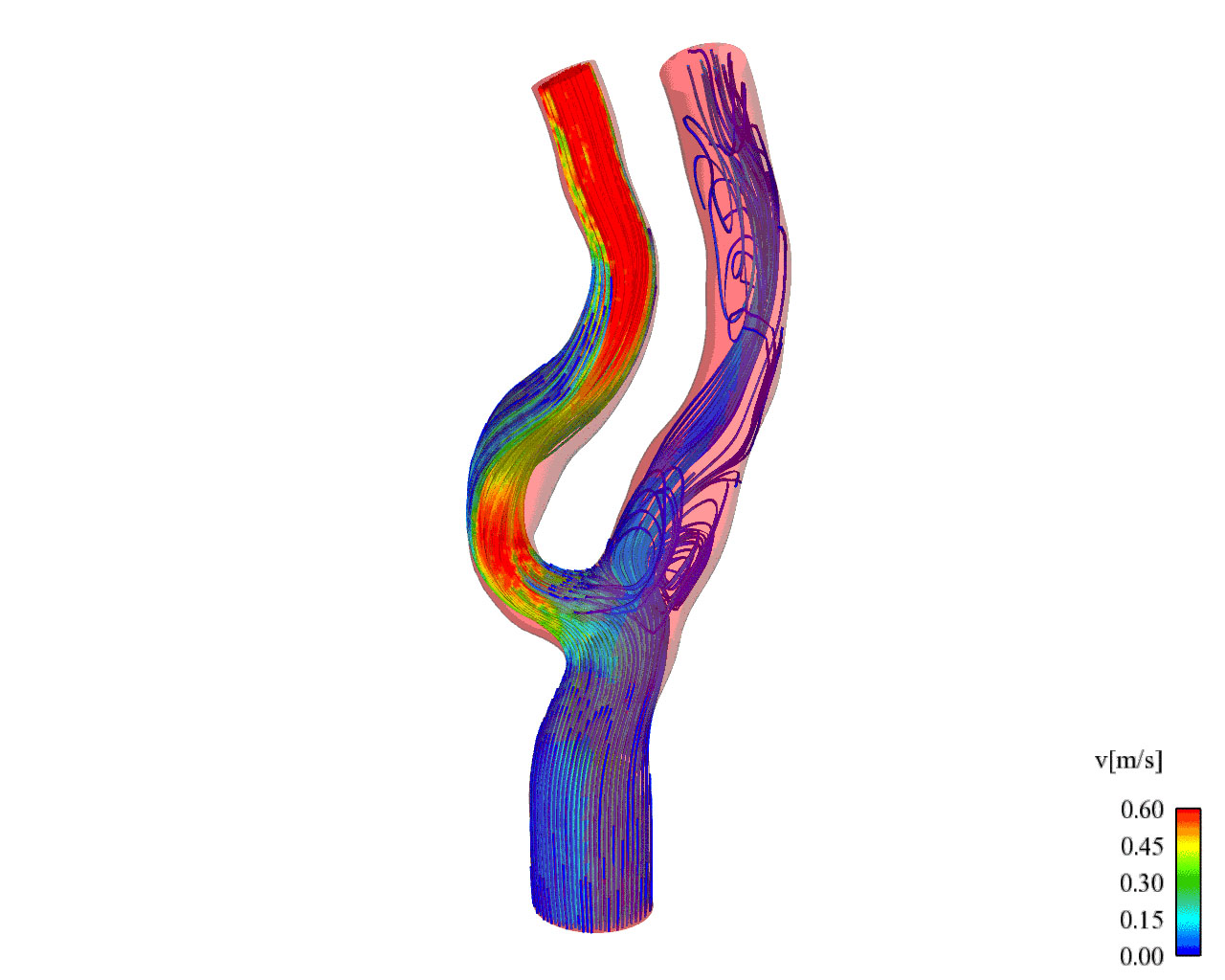 FSI Simulation of Carotid Hemodynamics |
For the fabrication of the self-expanding stent, the project counts with the collaboration of an EPO (Abbott vascular). As a final task of the project, the prototype will be evaluated in a pig model for its similarity with human. Success will be quantified tin terms of stenosis reduction, fibrosis proliferation in the short al long term, among others.
In addition to the advances that supposes a new design of carotid stent which overcomes the problems of current designs, there are additional benefits related with the project: i) a better understanding of mechanical factors influencing a successful angioplasty, ii) development of an advanced computational which allows to define and evaluate new guidelines for the design of other medical devices, and iii) consolidation of a multidisciplinary team which makes possible approaching this type of problems from a integrating perspective, a key point in biomechanics.
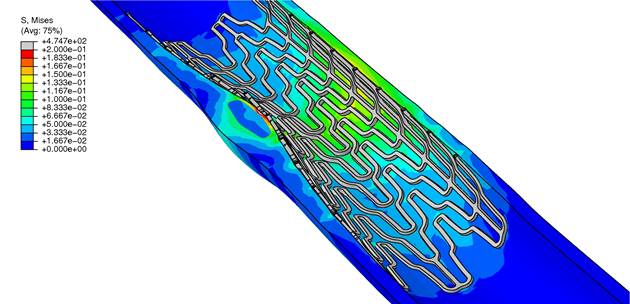 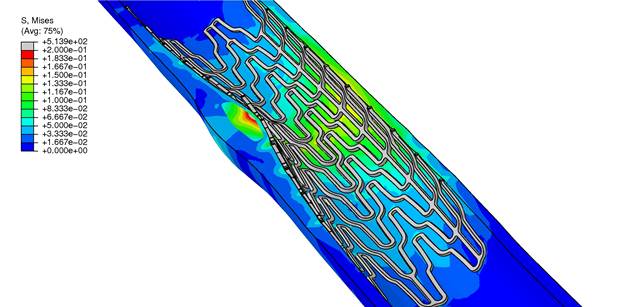 Computational simulation of stent deployment in fibrotic and lipid plaques |
Results from the animal experience of stent implantation in pigs |
PUBLICATIONS
Papers directly related with the projec
1. Numerical framework for patient-specific computational modelling of vascular tissue
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING
Alastrue, V; Garcia, A; Pena, E; Rodriguez, JF; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2010 Volumen: 26 (1), 35-51
2. On the use of the Bingham statistical distribution in microsphere-based constitutive models for arterial tissue
MECHANICS RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Alastrue, V; Saez, P; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2010 Volumen: 37 (8), 700-706
3. A constitutive formulation of vascular tissue mechanics including viscoelasticity and softening behaviour
JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
Pena, E; Alastrue, V; Laborda, A; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2010 Volumen: 43 (5), 984-989
4. Anisotropic micro-sphere-based finite elasticity applied to blood vessel modelling
JOURNAL OF THE MECHANICS AND PHYSICS OF SOLIDS
Alastrue, V; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M; Menzel, A
Año: 2009 Volumen: 57 (1), 178-203
5. On the use of non-linear transformations for the evaluation of anisotropic rotationally symmetric directional integrals. Application to the stress analysis in fibred soft tissues
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING
Alastrue, V; Martinez, MA; Menzel, A; Doblare, M
Año: 2009 Volumen: 79 (4), 474-504
6. The Effect of Material Model Formulation in the Stress Analysis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
ANNALS OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING
Rodriguez, JF; Martufi, G; Doblare, M; Finol, EA
Año: 2009 Volumen: 37 (11), 2218-2221
7. Experimental study and constitutive modelling of the passive mechanical properties of the ovine infrarenal vena cava tissue
JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
Alastrue, V; Pena, E; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 41 (14), 3038-3045
8. Modelling adaptative volumetric finite growth in patient-specific residually stressed arteries
JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
Alastrue, V; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 41 (8), 1773-1781
9. Removal of Retrievable Inferior Vena Cava Filters 90 Days After Implantation in an Ovine Model: Is There a Time Limit for Removal?
ARCHIVOS DE BRONCONEUMOLOGIA
de Gregorio, MA; Laborda, A; Higuera, M; Lostale, F; Gomez-Arrue, J; Serrano, C; Martinez, MA; Viloria, A
Año: 2008 Volumen: 44 (11), 591-596
10. Finite element implementation of a stochastic three dimensional finite-strain damage model for fibrous soft tissue
COMPUTER METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS AND ENGINEERING
Rodriguez, JF; Alastrue, V; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 197 (9-12), 946-958
11. Mechanical stresses in abdominal aortic aneurysms: Influence of diameter, asymmetry, and material anisotropy
JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICAL ENGINEERING-TRANSACTIONS OF THE ASME
Rodriguez, JF; Ruiz, C; Doblare, M; Holzapfel, G
Año: 2008 Volumen: 130 (2), 21-23
Papers indirectly related with the project12. Experimental study and constitutive modeling of the viscoelastic mechanical properties of the human prolapsed vaginal tissue
BIOMECHANICS AND MODELING IN MECHANOBIOLOGY
Pena, E; Calvo, B; Martinez, MA; Martins, P; Mascarenhas, T; Jorge, RMN; Ferreira, A; Doblare, M
Año: 2010 Volumen: 9 (1), 35-44
13. Application of the natural element method to finite deformation inelastic problems in isotropic and fiber-reinforced biological soft tissues
COMPUTER METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS AND ENGINEERING
Pena, E; Martinez, MA; Calvo, B; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 197 (21-24), 1983-1996
14. Computer simulation of damage on distal femoral articular cartilage after meniscectomies
COMPUTERS IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE
Pena, E; Calvo, B; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 38 (1), 69-81
15. On finite-strain damage of viscoelastic-fibred materials. Application to soft biological tissues
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING
Pena, E; Calvo, B; Martinez, MA; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 74 (7), 1198-1218
16. Prediction of nonlinear elastic behaviour of vaginal tissue: experimental results and model formulation
COMPUTER METHODS IN BIOMECHANICS AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING
Martins, P; Pena, E; Calvo, B; Doblare, M; Mascarenhas, T; Jorge, R; Ferreira, A
Año: 2010 Volumen: 13 (3), 327-337
17. Unraveling Changes in Myocardial Contractility During Human Fetal Growth: A Finite Element Analysis Based on In Vivo Ultrasound Measurements
ANNALS OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING
Pena, E; Tracqui, P; Azancot, A; Doblare, M; Ohayon, J
Año: 2010 Volumen: 38 (8), 2702-2715
18. On modelling damage process in vaginal tissue
JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
Calvo, B; Pena, E; Martins, P; Mascarenhas, T; Doblare, M; Natal Joro, RM; Ferreira, A
Año: 2009 Volumen: 42 (5), 642-651
19. An anisotropic pseudo-elastic approach for modelling Mullins effect in fibrous biological materials
MECHANICS RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS
Pena, E; Doblare, M
Año: 2009 Volumen: 36 (7), 784-790
20. On the Mullins effect and hysteresis of fibered biological materials: A comparison between continuous and discontinuous damage models
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SOLIDS AND STRUCTURES
Pena, E; Pena, JA; Doblare, M
Año: 2009 Volumen: 46 (7-8), 1727-1735
21. On modelling nonlinear viscoelastic effects in ligaments
JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
Pena, E; Pena, JA; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 41 (12), 2659-2666
22. Adaptive Macro Finite Elements for the Numerical Solution of Monodomain Equations in Cardiac Electrophysiology
ANNALS OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING
Heindenreich, E; Ferrero, J; Doblare, M; Rodriguez, JF
Año: 2010 Volumen: 38 (7), 2331-2345
23. Compact schemes for anisotropic reaction-diffusion equations with adaptive time step
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING
Heindenreich, E; Gaspar, FJ; Ferrero, J; Rodriguez, JF
Año: 2010 Volumen: 82 (8), 1022-1043
24. Fourth-order compact schemes with adaptive time step for monodomain reaction-diffusion equations
JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS
Heidenreich, EA; Rodriguez, JF; Gaspar, FJ; Doblare, M
Año: 2008 Volumen: 216 (1), 39-55